Diazonium Coupling (Diazo Coupling, Azo Coupling)
An azo
coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that
produces an azo compound. Nitrogen
is used to make a bridge between two benzene rings.
Dizonium compound + Aromatic compound = Azo
compound
This is basically an electrophilic aromatic
substitution reaction. Due to the positive charge on the terminal nitrogen of the -N=N+ group,
dizonium cation may participate as an electrophile. As a result,
two aromatic compounds are coupled by a -N=N- group. This is known as the azo group (diazo group). The corresponding
reaction is called diazonium
coupling (diazo
coupling, azo coupling).
Examples of Coupling Reactions:
1)
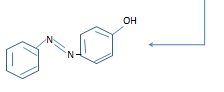
Reaction with Phenol
Phenol is
dissolved insodium hydroxide solution to give a solution of sodium phenoxide.
When this
phenoxide ion reacts with dizonium ion, an azo compound is formed in which two
benzene rings are linked by a nitrogen bridge.
2)
Reaction with Phenylamine (aniline)
The reaction
of aniline with dizonium salt produced a yellow solid known as aniline yellow.
Uses: Azo coupling is the most widely used industrial reaction in
the production of dyes, lakes and pigments.
Limitation: The electrophilicity of diazonium ions
is only relatively weak, as their positive charge is delocalized over the two
nitrogen atoms.
The unsubstituted benzenediazonium
cation may react only with strongly activated aromatic compounds, such as
phenolates and amines, The substitution normally occurs at the para position, except when this position is already occupied, in which case ortho position is favoured. .




No comments:
Post a Comment